This post contains affiliate links.
In this day and age, just about everyone uses wireless devices to send sensitive and personal information over WiFi.
The risk that comes with this activity is that it provides hackers with the opportunity to steal this information as it’s sent through the air between devices.
Thankfully, there are devices in your home network that can help protect you when you’re sending data wirelessly.
Your router is a perfect example of this.
So how does your router protect your personal information that’s sent over WiFi? Does a router encrypt your data, or is there a different way that it protects your communications?
In general, all modern routers encrypt communications with devices connected to their wireless networks. Encrypting communications between devices on the network ensures that data sent over WiFi cannot be read by nearby devices that are not intended to receive it.
In this post, I’ll break down how routers protect their communications using encryption. I’ll also talk about how you can verify that your router’s encryption settings are configured correctly.
How Do I Know if My Router Is Encrypted?
When it comes to router encryption, I have some good news and bad news.
I’ll start with the good news first.
The good news is that your router most likely has encryption enabled by default. In other words, your router will automatically encrypt communications between it and your devices.
And the bad news?
The bad news is, even if your router has encryption enabled, your data might not be totally safe.
The reason for this is because the safety of your devices’ communications depends upon the type of encryption that your router is using.
Unfortunately, not all encryption is created equal.
The fact is, some encryption methods don’t do a great job of protecting your data because they can be cracked by hackers.
For example, if a given encryption key isn’t strong enough, hackers can actually reverse engineer the encryption key that’s being used. Once they’ve figured out the encryption key used in a message transmission, they can read the messages between your device and your router.
It doesn’t matter that the communication was encrypted.
So even if your router has encryption enabled, you need to verify that the right encryption settings are in place.
If any of this information is confusing to you, don’t be overwhelmed. The next sections will hopefully clear up any confusion you have.
How Does Router Encryption Work?
When it comes to protecting your data, your router has quite a bit of functionality.
Of utmost importance is it’s ability to protect the data that’s sent between it and your devices.
This is where encryption comes in.
So how exactly does a router encrypt your data?
Router encryption starts with the identification of the devices it trusts. Although this might sound complicated, it’s really not.
Your router trusts the devices that’re able to connect to it by providing the correct password for its wireless networks. After all, the only devices that’re connected to a router in the first place should be the ones that have been trusted with the password for the network.
This highlights the need for unique passwords for your router’s wireless networks, but that’s a topic for a another time.
When a device joins a router’s wireless network, an encryption key is established between the device and the router. This encryption key is used to scramble the data that the two devices send to each other.
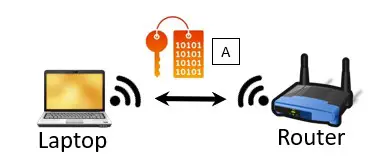
Think of the encryption key like a decoder ring.
When data is sent from a device to the router, the decoder ring is used to scramble the message. When the router receives the message, it uses the same decoder ring to translate the message so that it’s readable.
This is what prevents a hacker or malicious user from listening in on your device’s conversation with your router. They’re welcome to listen in on the conversation between your device and your router, but the messages won’t be useful.
In other words, the hacker doesn’t have access to the decoder ring that your device and router used to scramble the message.
To make things more secure, each device that connects to the router will have a different encryption key (or decoder ring) to scramble the data between the two devices.

On top of that, depending upon the type of encryption that’s used, the router and device connected to it will periodically change the decoder ring they’re using.
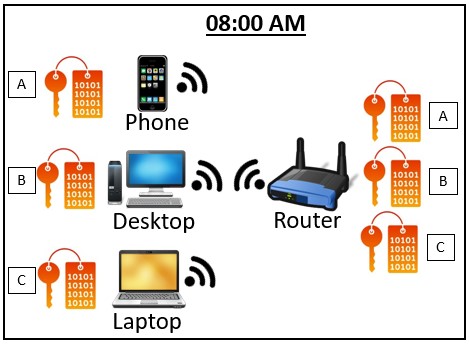
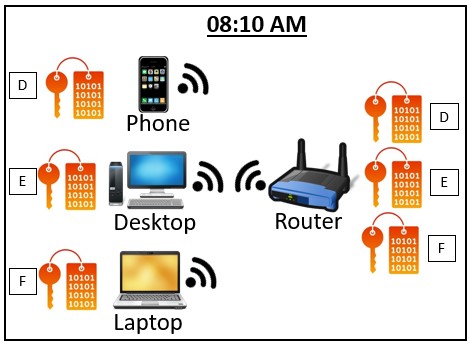
Talk about a headache for anyone that’s trying to listen in on the conversation.
That’s exactly the point.
What Does Router Encryption Protect?
There’s an important distinction that needs to be made when it comes to your router’s ability to encrypt communications with your devices.
You need to understand that router encryption will only protect communications on your local network. To put this another way, your router’s encryption will not protect your devices’ communication on the open internet.
Let me break this down.
As I previously mentioned, when a device joins a router’s network, the device and router share an encryption key.
The key here (pun intended) is that this encryption key only protects WiFi communication between that device and the router.
Any communication that happens beyond the device and router communicating directly with each other isn’t protected by the router’s encryption.
For example, when a router sends an internet request to a router, the router only encrypts the request coming to the router. Once that request is passed to the public internet, the request is no longer protected by the router’s encryption. That’s because this communication isn’t happening over WiFi. It’s happening over the internet’s backbone of wired connections.
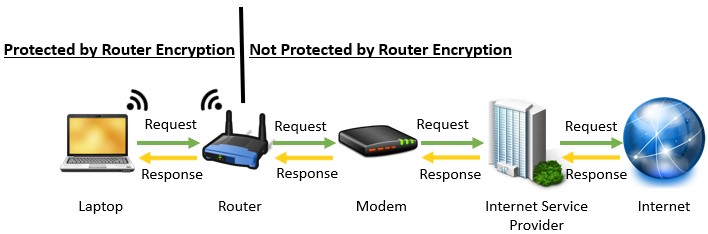
To put this another way, if your device is accessing a website on the internet, this traffic could still potentially be stolen by hackers on the open internet.
There’s a totally separate encryption method for communication between devices and web pages, which is called Transport Layer Security (TLS).
If TLS is in place on a website, the communication between your device and the website will be protected as well.
TLS is a topic for another post, but the bottom line here is that you should recognize that a router using encryption doesn’t mean all your traffic is protected.
It just means that the local communication over WiFi between the router and device will be protected.
How to Check Your Router’s Encryption Settings
If you’re not sure what your router’s encryption settings are, you should verify that it has the proper encryption configuration is in place.
There’s too much at stake with your personal data to risk not encrypting your data with the strongest encryption keys.
To do this, you first need to access your router’s settings.
If you’re not sure how to log in to your router’s settings, fear not. I have included the necessary steps for logging in to your router in a previous post I’ve written about updating your router. Check out this post for guidance on how to log in to your router’s settings.
Once you’ve logged in to your router’s settings, you need to go to the Advanced Settings tab.
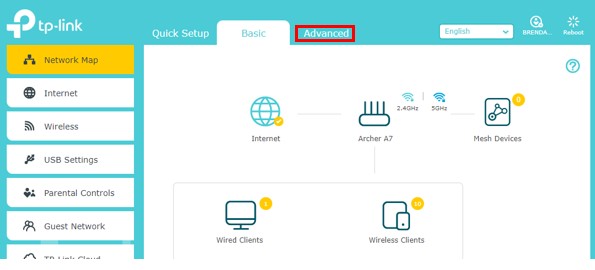
In the Advanced settings tab, I had to go under the “Wireless” header and select “Wireless settings”. This brought me to my router’s encryption settings.
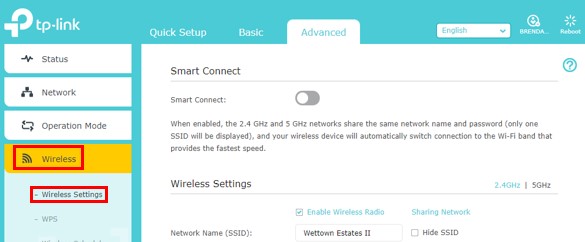
Accessing your router’s encryption settings might be slightly different for you depending upon the make and model of your router. With that said, it’s a safe bet that the encryption settings will be in the Advanced settings section.
Now that you’ve accessed your router’s encryption settings, we need to make sure they’re set correctly.
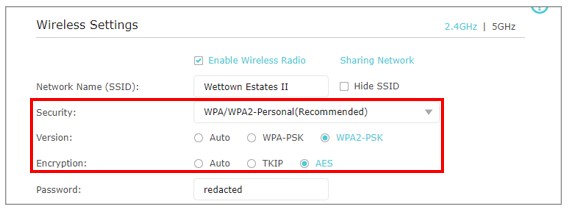
The settings you should have in place on your router are as follows:
- WPA/WPA2-Personal for the security setting. If the router you’re configuring is for your home network, you’ll want to select “Personal” here. The “Enterprise” security version is for routers that are used in businesses and offices.
- WPA2-PSK (WiFi Protected Access 2 Pre-Shared Key) for the encryption version. WPA2 was developed more recently than WPA-PSK and it provides security advancements to better protect your communications.
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for the encryption algorithm. This is the strongest available encryption algorithm available.
As a side note, you don’t want to select “Auto” for any of these options.
When Auto is selected, it lets the device determine the encryption method and algorithm that’s used.
You want to ensure that the strongest encryption standards are always used for communication between your devices and your router. That’s why you should explicitly select the settings above. This puts your router in control of the encryption methods used to protect your data.
Wrap Up
At this point, you should be able to access your router’s settings and ensure that the strongest encryption settings are in place.
If you have any questions about the information presented in this post, please drop a comment below.
For more fascinating information on similar topics, check out these other posts I’ve written:
Will a New Router Increase Internet Speed? An Explanation
What Speed Can My Router Handle? What You Need to Look At
Do You Need an Internet Connection if You Have WiFi?
