This post contains affiliate links.

When buying an ethernet cable, there are several factors to consider. For example, there are multiple categories of cable to choose from, and each of these cable types comes in many different lengths. You can even buy kits that allow you to make ethernet cables as long as you want.
When making these decisions, it’s important to understand the impact that each may have on your network. The last thing you want to do is buy an ethernet cable that limits your internet speed.
A common question I’ve seen has to do with the length of the ethernet cable you use, and how the length of an ethernet cable will affect the speed of your network.
For the most part, this is an easy answer:
In general, the length of an ethernet cable doesn’t affect the speed of your network as long as it’s less than 328 feet (100 meters) long. If an ethernet cable is longer than 328 feet, its data transfer speed will be significantly reduced and it will restrict the performance of your network.
With that said, the type of ethernet cable you’re using will also come into play. Some types of ethernet cables (like category 6, 7a, and 8 cables) are designed to support different speeds at different lengths. You need to know the speeds that these cables support at different lengths to make sure you’re using the right one for your network.
In this post, I’ll provide you with all you need to consider when it comes to the length of ethernet cables and their impact on your network speed.
How does an ethernet cable transmit data?
First things first.
Understanding how ethernet cables send data will help you understand how the length of an ethernet cable impacts the speed of your network.
After all, that’s the whole purpose of ethernet cables in the first place. To move data from one device to another so the devices can communicate with each other.
So how do ethernet cables transmit data?
Ethernet cables are made up of pairs of copper wires that are twisted together inside the cable. Here’s a picture of what the inside of an ethernet cable looks like:
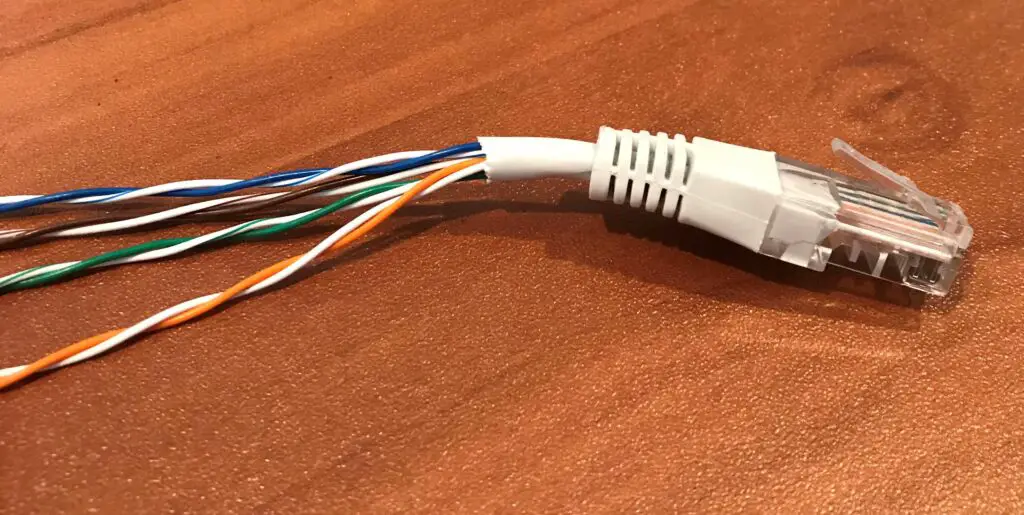

When provided with an electrical signal, these wires send electric pulses from one end of the cable to the other.
If a system on one end of the cable needs to send data to the system on the other end, it’ll convert the data it wants to send into a series of electric pulses. These electric pulses are sent to the other system through the cable.
When the signals reach the receiving system, they’re translated back into the original data that the sending computer sent.
This is how data is transmitted using ethernet cables.
How fast does an ethernet cable transmit data?
Now we know how ethernet cables transmit data.
But how fast does this happen?
Fast. Really fast.
Think about what’s happening here. The data being transferred by the ethernet cable has been converted to electric current. This electric current travels through the copper wires in the cable at about 64% as fast as the speed of light.
To be exact, that means data is traveling on the ethernet cable at around 192 kilometers per second (km/s). This is how fast data moves on all types of ethernet cables.
Yeah, I’d say that’s pretty fast.
Keep this information in mind as it’s important for the next section.
As a side note, if you’re wondering why data can move so fast on ethernet cables but different cables support different transmission speeds, it has to do with the amount of data a cable can transfer at a given time. This term is called the cable’s frequency, which is related to the thickness of the copper wires inside the cable.
Does the length of an ethernet cable affect its speed?
Now that I’ve given you all this background information, hopefully I can make it clear why it’s important.
So the question we’re trying to answer is if an ethernet cable’s length affects its data transmission speed.
To answer this question, let me refer you back to what we just talked about. Once data is translated into an electric signal, it travels over an ethernet cable at the speed of 192 km/s.
With data traveling that fast, do you think it makes a difference how long the cable is?
The answer here is no.
The electrical signals on an ethernet cable travel so fast that it doesn’t matter if you’re using a really long cable. When it comes to ethernet cables, there are no disadvantages to using long cable lengths.
On the other hand, are there advantages to using short ethernet cables?
Are shorter ethernet cables faster?
Spoiler alert: there are no advantages to using a shorter ethernet cable.
Due to the fact that electricity is traveling at very fast speeds along the copper wire of the cable, you won’t be able to notice a difference if one ethernet cable is shorter than the other.
Let’s use an extreme case to illustrate this.
In our imaginary experiment we’ll use one category 5e ethernet cable that is 300 feet long and another that is 1 foot long.
In this test let’s say you have two computers that are exactly the same. One computer is connected to your router with the 300 foot long cat 5e cable. The other is connected to your router with the 1 foot cat 5e ethernet cable.
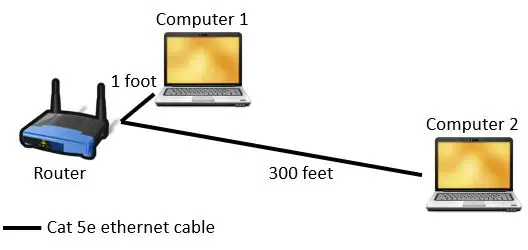
If you used both computers to navigate to YouTube and started streaming the same video, you wouldn’t notice a difference in performance between the two computers.
Technically, the internet data you requested (i.e. the YouTube video) would reach the computer with the 1 foot ethernet cable faster. However, data travels so fast over ethernet cables that the data would reach the computer with the shorter ethernet cable fractions of a second ahead of the computer connected with the long cable.
From your perspective, the internet experience on both computers would be the same.
For another visual, look at the picture below. Using the cable on the left will provide the same performance as the cable on the right.

Sounds great, doesn’t it? There really aren’t any disadvantages to using long ethernet cables are there?
Unfortunately it’s not as straightforward as it may seem. That’s because there’s a limit to the length that an ethernet cable can be before its speed is affected.
There are two things to consider here:
- All ethernet cables will experience much slower speeds if they’re too long
- Some ethernet cables are designed to support different speeds at different lengths
Let’s take a closer look at both of these situations.
Ethernet cable performance degrades at long lengths
As I previously mentioned, in most cases the length of your ethernet cables doesn’t affect their speed.
Unfortunately there’s a limit to this. That’s because the performance of almost all ethernet cables degrades when the cable is about 328 feet (100 meters) or longer.
Let’s say you have a standard cat5e ethernet cable. These cables generally support data transmission speeds up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps).
If that cable is 200 feet long, it won’t have any trouble supporting speeds up to 1 Gbps. Add another 128 feet or so to that cable, and it’s an entirely different story.
Although I’ve never tried it myself, I’ve read that data transmission speeds of cat5e ethernet cables can drop to around 10-15 megabits per second (mbps) when the cable is longer than 328 feet.
According to my calculations, that’s about a 98% drop in performance. I think you’d notice the difference.
But why does this happen? Why do cables get much slower at about 300 feet long?
This is due to the fact that ethernet cables have resistance.
The longer the ethernet cable is, the more resistance the cable has to the flow of electricity. In other words, the longer the cable is, the harder it is for the electric pulses to travel from one end of the cable to the other.
At around 328 feet, the resistance of the cable becomes too much for the electricity running through the cable, greatly slowing it down. This could actually happen at shorter lengths than 328 feet if there are sources of electromagnetic interference affecting the cable.
The good news is, most people don’t need ethernet cables that are longer than 328 feet. If you do, just buy two shorter cables and connect them with an ethernet coupler.
Some ethernet cables are designed to support different speeds at different lengths
The other factor to be aware of when it comes to ethernet cable performance has to do with the type of ethernet cable you have. That’s because some ethernet cable types support different speeds depending upon how long they are.
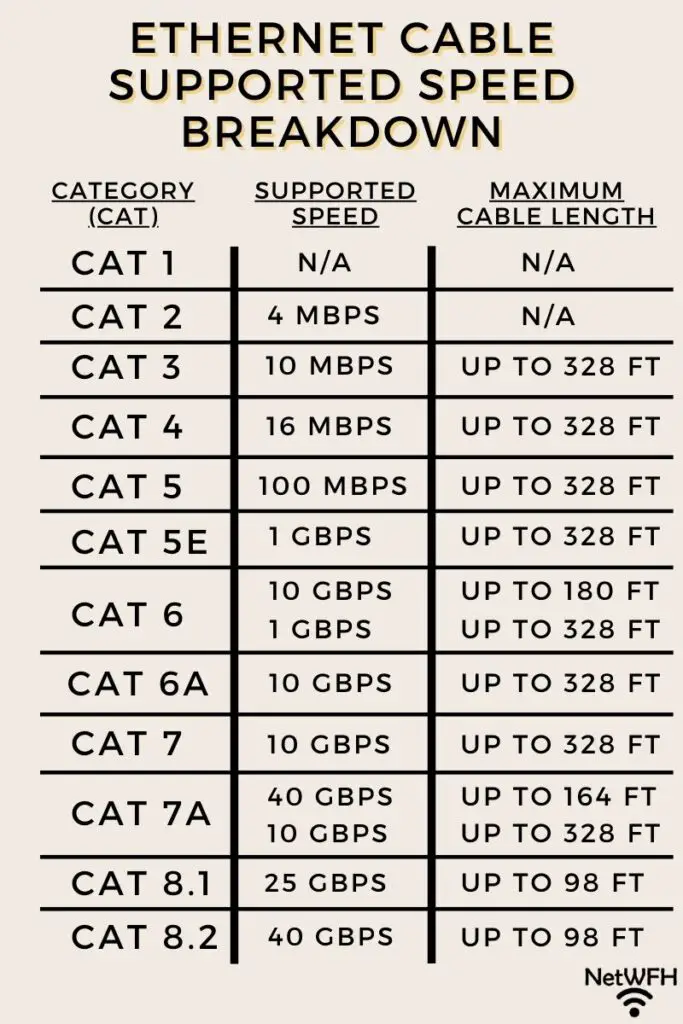
Let’s start with the most common ethernet cables. These are category 5e and category 6 cables.
Do these cable types supports different speeds at different lengths?
Category 5e cables will support the same speed for any length up to 328 feet. The same can’t be said for cat 6 ethernet cables.
Cables that support different speeds at different lengths
A category 6 ethernet cable will support speeds of 10 Gbps for up to 180 feet (55 meters). At distances longer than 180 feet and less than 328 feet, a cat 6 cable supports speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Chances are, you won’t need an ethernet cable longer than 180 feet. Even if you did, 1 Gbps should cover any of your data transmission needs.
To put it simply, this information probably won’t change the type of ethernet cable you use. You’d only need a cable that supports faster speeds if you’re using it in some sort of data center.
Speaking of data centers. That’s exactly what these next cables are used for.
The other ethernet cables that support different speeds at different lengths are the category 7a and category 8 cables.
A cat 7a ethernet cable supports speeds of 40 Gbps up to 164 feet (50 meters). For cat 7a cables between 164 and 328 feet, they support data transmission speeds up to 10 Gbps.
Category 8 cables are a little different. Both types of cat 8 cables (8.1 and 8.2), support high data transmission rates of 25 Gbps and 40 Gbps, respectively. What’s unique about these cables is that they’re designed to be a maximum length of 98 feet. So although they don’t support different speeds at different lengths, their maximum length is much shorter than other ethernet cables.
All other types of ethernet cable will support the same speed for any length up to 328 feet. So if you have a cat 5e ethernet cable, you don’t have to think twice about the speed it supports.
Wrap up
As long as your ethernet cables aren’t longer than 328 feet and they aren’t cat 6, cat 7a, or cat 8 cables, it doesn’t matter how long they are. They’ll support the same data transmission speeds.
This’ll make things easier when you’re setting up your internet connections. You’ll have the freedom to use the length of ethernet cable that best fits your situation.
In fact, most people don’t use ethernet cables longer than 20 or 30 feet. Cables of that length will all support the maximum possible data transmission rate of the cable, even for cat 6, cat 7a, and cat 8 cables.
For the most part, there’s really not much to worry about when it comes to ethernet cable lengths and the speeds they support. Odds are, you’re using a cable that’s well within its performance limits.
If you have any questions about this information or you’d like to share your personal experiences with ethernet cables, please drop a comment below.
If this was useful information for you, check out some of my other posts on similar topics:
How to Tell What Type of Ethernet Cable You Have
Can an Ethernet Cable Slow Your Internet Speed?
Is an Ethernet Cable Faster Than WiFi?
