This post contains affiliate links.

If you search online for an ethernet cable to buy, you get hit with a lot of terms and specifications.
Take this ethernet cable for example. If you look at the title of the cable on Amazon, I count about 8 characteristics that are listed:
- Cat6
- Stranded
- 550 Mhz
- UTP
- Pure bare copper wire
- 24 AWG
- 5ft
- Black
Getting hit with all these specifications at once can be overwhelming. It makes it really hard to pick out which ones are important, especially if you’re not super technical.
What I found interesting is that of the 8 characteristics listed in the example above, two of them pertain to the frequency that the cable operates at.
This immediately raises some questions.
Does this mean frequency is an important characteristic of ethernet cables? Should you be paying attention to the frequency the cable supports when deciding which one to buy?
Actually, the frequency of your ethernet cables is very important. The higher the frequency a given ethernet cable supports, the faster it can transfer data. The faster a cable can transfer data, the higher the maximum data transfer speed the cable will support.
In this post, I’ll dive into everything you need to know about the frequencies of ethernet cables. I’ll talk about why the frequency supported by a cable is important, as well as what frequency you can expect when buying your ethernet cables.
With that said, let’s take it from the top.
What does frequency refer to in ethernet cables?
Before we look at the different frequencies supported by ethernet cables, it’s important to have an understanding of what frequency means in this context.
If you look up the definition of frequency, it’ll be defined as the number of repetitions of a periodic process in a unit of time.
Ok, so what does that mean for ethernet cables?
To answer this question completely, we’ll have to take a step back for a minute.
How ethernet cables transfer data
To understand how the frequency of an ethernet cable is measured, we need to first go over how they transfer data.
Don’t worry, I’ll stay out of the nitty gritty technical details here.
To start, it’s important to know that your ethernet cables are made up of copper wires. Slice any of your ethernet cables open, and you’ll see they have 8 wires inside them.
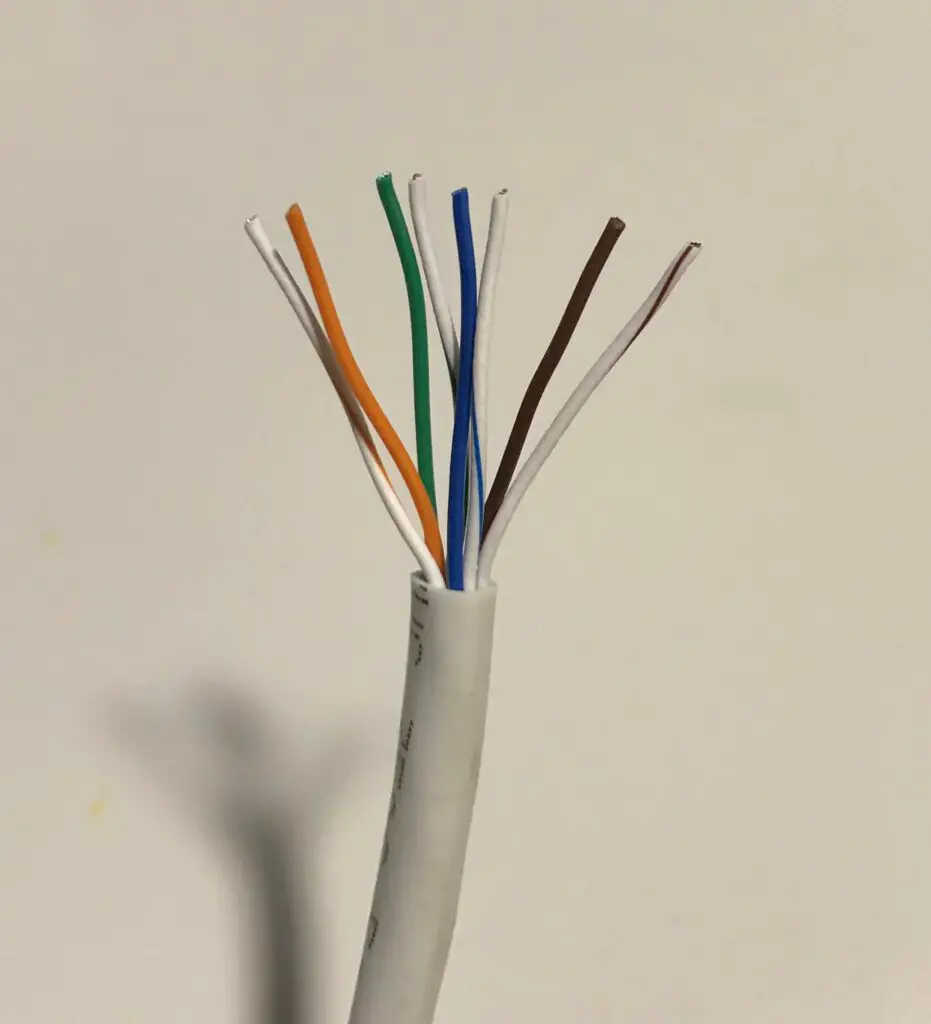
These 8 wires are used to send and receive data from both ends of the cable. Data can move in both directions.
Data is moved by sending electronic signals from one end of the cable to the other. This is why the wires inside your cables are copper. Copper is a good conductor of electricity.
It’s almost as if they designed it that way on purpose.
Anyway, back to the topic at hand.
The other important piece of this is that computers and other devices speak to each other in 1s and 0s. This is called binary code. In other words, data passed from one device to another through an ethernet cable will be a series of 1s and 0s.
Data is sent over ethernet cables with pulses of two separate voltages. One voltage represents a “0”, while the other voltage represents a “1”.
As the device on the other end of the cable receives these voltages of electricity, it translates the voltages into binary data so it can understand the message.
This is where the frequency of the cable is important.
Why frequency is important for ethernet cables
Ok, so data is sent over ethernet cables by sending pulses of two different voltages to the other end.
Frequency refers to how fast your ethernet cable is able to do that.
In ethernet cables, frequency refers to how many times the ethernet cable can change its state in 1 second. In other words, it describes how many times an ethernet cable change between the two pulses of voltage sent over its wires.
To put this another way, think of your ethernet cable as an author.
In this analogy, the frequency of your ethernet cable would be reflected by how fast the author can typee.
The more words an author can type in a minute, the faster he or she will be able to finish their book.
If one author can write 60 words per minute, and another can write 80 words per minute (with the same quality), the writer that can write 80 words per minute will finish the book faster.
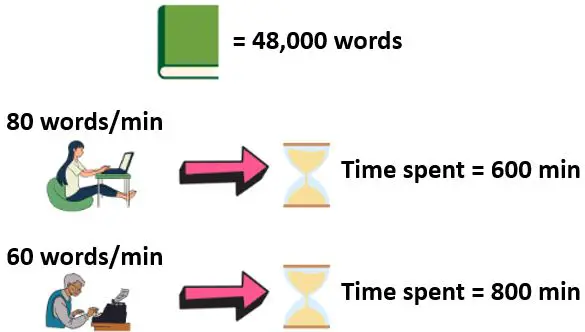
In this scenario, the author that can write 80 words per minute is the better choice.
To bring this analogy back to ethernet cables, it’s easiest to think about an ethernet cable’s frequency as how fast a given cable can write.
The more times it can change its state in 1 second, the faster it can write data.
For the record, ethernet cables can write really fast.
That’s why a cable’s frequency is measured by how many millions of times they can change their state in a second. The unit of measurement for ethernet cable frequency is Megahertz (MHz).
Does your ethernet cable’s maximum frequency matter?
Based upon the information above, it’s pretty easy to tell what you want in an ethernet cable.
The higher the frequency it can support, the faster a cable can process data through it.
The faster a cable can process data, the more data it can send in a given amount of time.
The more data it can send in a given amount of time, the higher the data transfer speed it can support.
I think you can see where this is going, right?
The higher the frequency a cable can support (in MHz), the faster it can send data from one end of the cable to the other.
What you’ll see when looking at ethernet cables is that frequency and the maximum data transfer speed supported by the cable go hand in hand. The higher the maximum frequency of a cable, the higher the maximum data transfer speed it’ll support.
So how should you go about finding the ethernet cables that support the highest frequencies?
This is actually easier than you think.
That’s because each category of ethernet cable has a defined maximum frequency it operates at.
Let’s take a closer look at the factor that determines the maximum frequency a cable can support.
What affects the maximum frequency of an ethernet cable?
Different categories of ethernet cables support different frequencies and speeds.
The question is, what makes them able to do this? What is it about ethernet cables that determines the frequency and speed they can support.
It all comes down to the copper wires inside the cables.
As I previously mentioned, ethernet cables transfer data by sending pulses of electricity through the copper wires in the cable.
The thicker these copper wires are, the more electricity they’re able to pass through them at a given point in time.
The more electricity you can pack into a cable at a given point in time, the higher the frequency it can support.
So does this mean cables that can support higher frequencies have thicker copper wires inside them?
You bet it does.
Copper wire standards
The thickness of copper wires inside an ethernet cable is measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG).
AWG ranges from 0000 AWG to 40 AWG. Calculating the AWG number of a wire is a little complicated, but all you need to know is that the higher an AWG number is, the thinner the copper wire is.
In other words, 40 AWG is the thinnest standard size of a wire. 0000 AWG is the thickest.
The AWG value refers to a single wire, so each of the 8 wires inside an ethernet cable will have the same AWG.
AWG values
Here are the AWG values for the ethernet cables commonly used today. I’ve excluded cat7 cables from this table because they aren’t widely used (I’ll explain this later on):
| Category | AWG |
| Cat5e | 24 |
| Cat6 | 24 or 23 |
| Cat6a | 23 |
| Cat8 | 22 |
Unsurprisingly, the higher category ethernet cables have thicker copper wires inside them.
One important note here is that these measurements of thickness don’t include the color-coded plastic insulation surrounding the wire. It only refers to the thickness of the copper wire itself.
Here’s an example.
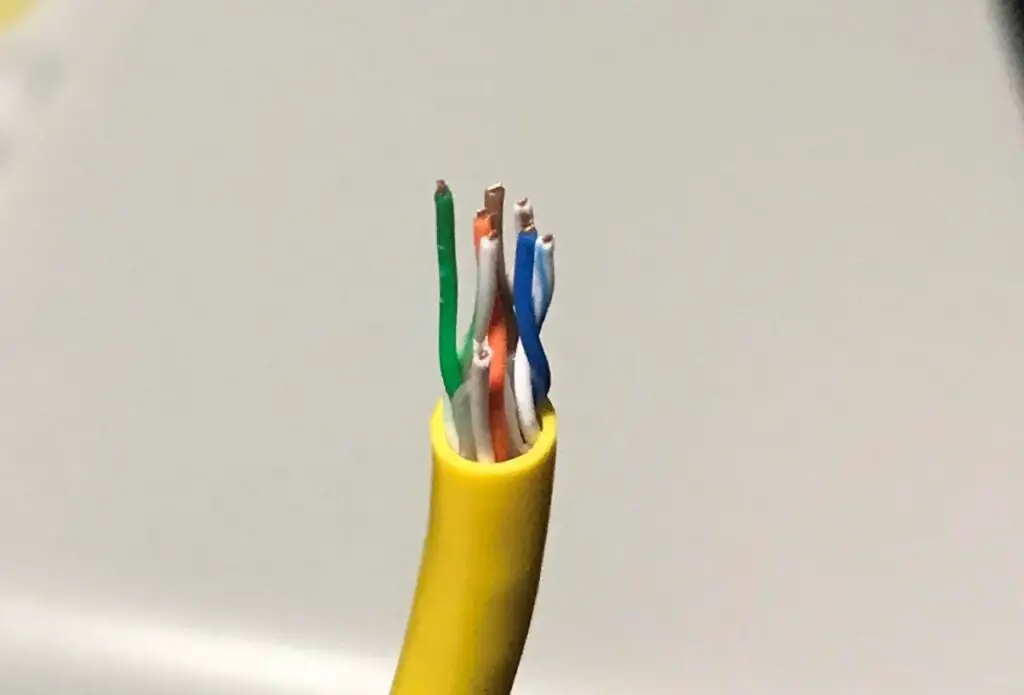

If you look closely, you can see the copper wires inside the color-coded insulation. The thickness of those wires is measured and assigned an AWG value.
That should give you an idea of how thin these wires really are.
You should also note that small changes in AWG can lead to significant differences in the frequency (and speed) a cable can support.
As you’ll see in the next section, a cat6 cable can support a maximum frequency that’s more than double what a cat5e cable can support. What’s crazy is that cat6 copper wires are only .05mm wider (.57mm versus .052mm).
The point here is that making the copper wires in an ethernet cable only slightly thicker will greatly increase their performance.
Speaking of performance, at this point I’m sure you’re wondering what frequency each category of cable supports.
Let’s take a closer look.
What is the frequency of each category of ethernet cable?
Each category of ethernet cable has a specific set of characteristics that they’re made to.
The specifications for each category of cable have been assigned and approved by the Electronic Industries Association and the Telecommunications Industry Association, also referred to as the TIA/EIA.
By standardizing the manufacturing of ethernet cables, it ensures all cables are made the same way.
This is why you can expect your ethernet cable to support a certain frequency, based upon the category of cable it is.
With that, let’s break down what we can expect from each category of ethernet cable:
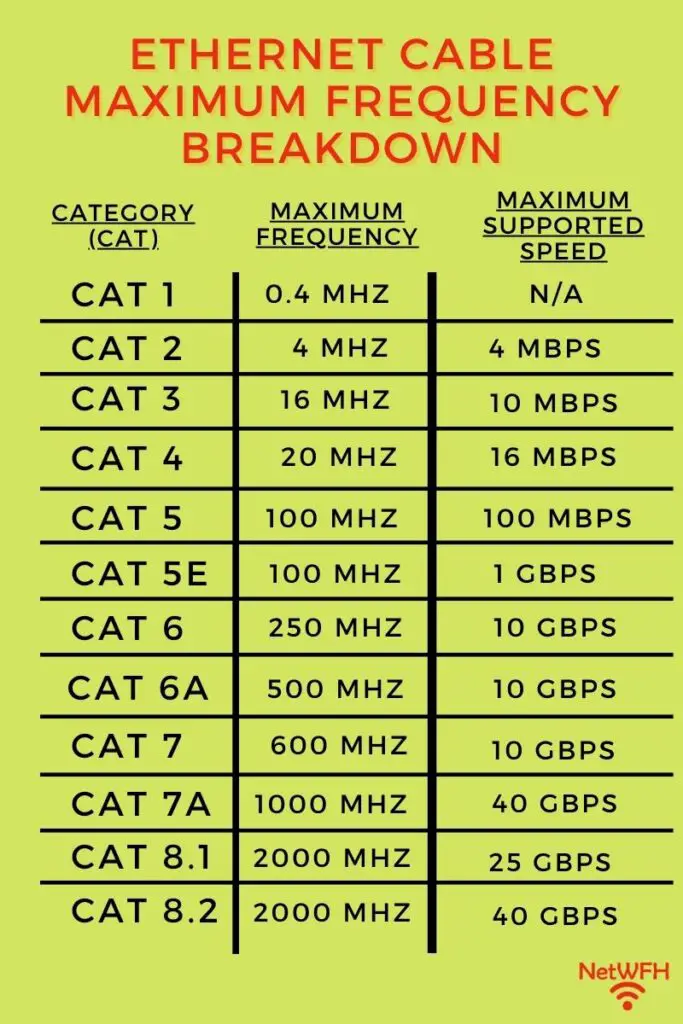
As you can see, the results are just as I described earlier.
The higher the frequency a cable can support, the faster the maximum speed it can support as well. You’ll see that as each category of cable increases, so does its supported frequency and speed.
There are a few exceptions, however.
Category 7 and 7a cables
The exceptions to this are category 7 and 7a cables.
Although these cables appear like they support speeds as fast or faster than category 8 cables at lower frequencies, there’s a catch.
These categories of cables aren’t recognized by TIA/EIA as official categories of cables.
In fact, in order to operate at the frequencies and speeds detailed in the figure above, category 7 and 7a cables wouldn’t be compatible with all the other categories of ethernet cables.
I’ll spare you all the details here, but the bottom line is any cat 7 or cat 7a cables you see today will perform to the same specifications as category 6a cables.
The main idea to take away from all this is that cables operating at higher frequencies will support faster speeds.
So as long as you use ethernet cables that support the speed of your internet plan, you won’t really need to worry about the frequency it supports. You know it’ll be sufficient because of how closely linked the maximum frequency and maximum speed of ethernet cables are.
Wrap up
Now you know the importance of frequency when it comes to the performance of ethernet cables.
The good news is that you don’t really have to worry about the frequency a cable can support when you’re buying your cables. In buying a certain category of ethernet cable, you’ll know the maximum frequency and speed it can support.
If you found this information helpful, check out some other posts I’ve written about similar topics:
Do the Colors of Ethernet Cables Matter?
How Long Do Ethernet Cables Last?
What Does Cat Mean for Ethernet Cables?
