
We have previously discussed whether your modem or ethernet cables have an impact on your internet, but what about routers? Does a router affect your internet speed as well, or is it only these other components that we have to worry about?
A router can affect the WiFi speed of a home network. If a router is used that does not fit the needs of the network and the internet plan that is in place, it can greatly reduce the speed of the entire network.
Routers can affect your WiFi speed if:
- Your router is older and doesn’t support the internet plan you have
- You place your router in the wrong location in your home or office
- The channel your router is communicating on is congested with other traffic
- You have not updated your router’s firmware to the most recent version
In this post we’ll dig into each of these scenarios in more detail and provide tips to ensure you’re getting the most out of your router.
What Is the Purpose of a Router?
Before we detail how a router can affect your internet speed, let’s start with the basics.
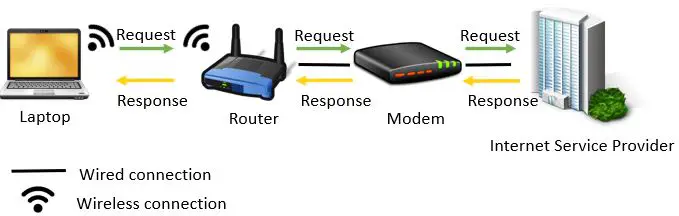
A router is a piece of equipment that’s used to help your devices connect to the internet.
Here’s a picture of my Archer A7 router. If you have a standalone router it’ll probably look similar to this.

Your router works in tandem with your modem. You need both of them in order to use the internet. That’s why you may see modems and routers combined into one device when you shop for them online.
Routers Coordinate Requests From the Devices on Your Network
Your router identifies where your internet requests should be sent to, and your modem translates the requests so they can be sent over the internet to the right destination. If you need a refresher on how modems work, check out my previous post this topic: Does Your Modem Affect Your Internet Speed?
Without a router, the requests sent by your devices wouldn’t get sent to the right destination and you wouldn’t be able to do anything on the internet.
In this sense, a router is like a post office. It slaps an address on all of your outgoing requests so this “mail” arrives where it’s supposed to.
Routers Provide a Wireless Network for Wireless Devices
More often that not, the routers that you see in home and office applications are wireless. This means that internet devices can communicate with them and connect to the internet without using ethernet cables.
How much of a pain would be it to connect all your internet devices (tablets, smart TVs, laptops, etc.) to your router with a wire?
Yeah I wouldn’t want that either. Thankfully your router has you covered.
Wireless routers take the data that your modem has received from the internet and sends it over radio signals (WiFi) to your devices. When your devices send requests to the internet, they send them via WiFi to the router. Your router then passes this information to your modem to be translated and sent over the internet.
How Does a Router Affect Your WiFi Speed?
Routers are vital to your internet connection. As a result, you need to make sure it’s not a bottleneck to your network.
Let’s take a look at the different ways your router can affect your internet speed.
What Happens if a Router Doesn’t Support Your Internet Plan
Since WiFi was created in 1997, many advancements have been made to the technology and new standards have been created. WiFi standards are created by a group called the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The standards themselves are referred to as the IEEE 802.11 standards.
I won’t get too far into the specifics of each standard in this post, but it’s important to understand the internet speeds that each standard supports.

Why are these WiFi standards important?
The reason it’s important to know these standards is because routers are built to support them. If you have an old router it may be built for older WiFi standards. When a router is built to old WiFi standards, it may not be able to support the bandwidth you’re paying for from your internet service provider (ISP). If this is the case, your router will be limiting the speed of your internet connection.
In general, not having the right router can have the biggest impact on your WiFi speed. A router that’s not built to support your internet speeds will slow down the internet for all of your wireless devices, because they all share the bandwidth that your router puts out over WiFi. You need to make sure you get this right.
To help visualize this, let’s look at a few examples.
Example of Router Limiting WiFi Speed
Let’s say you have a router that’s built to older WiFi standards, for example a Linksys Wireless G-Broadband router. Referring back to the ultimate 802.11 standards guide diagram above, you can see that a router built for 802.11g has a maximum speed of 54 megabits per second (Mbps).
What if you were paying for an internet plan that provided 200 Mbps?
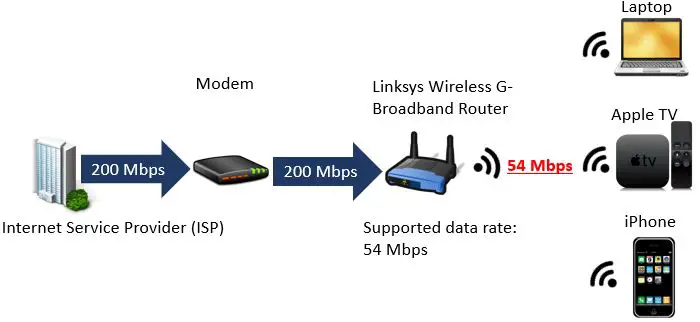
In this case even though you’re paying for 200 Mbps, you’re only getting 54 Mbps to share among all your wireless devices. To put it simply, you’re wasting your money paying for a 200 Mbps internet plan because your router can only handle 54 Mbps.
In this case, if you wanted to get the speed that you were paying for, you’d need a router built to (at least) the 802.11n standard.
Routers Do Not Increase Internet Speed
What if we looked at another scenario where you had a Linksys AC1900 router. This router is built to the 802.11ac standard which provides a maximum speed of 1.3 Gbps (on the 5GHz frequency band).
Let’s say you were paying for the same internet plan as the previous example that provided 200 Mbps. How much bandwidth would you have to share among all your devices?
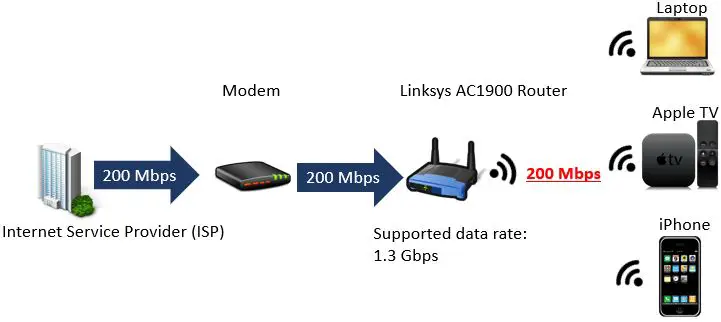
As you can see in the above diagram, just because your router is built to support faster internet speeds than what your ISP is providing, it won’t increase the speed of your connection.
This isn’t necessarily a bad thing though. In this example if you were to upgrade your internet plan in the future to gigabit internet (1 Gbps), you wouldn’t need to buy a new router as well. This is called “future proofing”.
As you can probably tell by now, you want to make sure your router can support at least the speed that your ISP provides.
It’s also safe to say that 802.11 standards will continue to improve as time goes on, and internet speeds will only get faster (and cheaper). As a result, it’s usually a smart move to buy a router that has some buffer in terms of the bandwidth it can support. This will allow you to upgrade your internet plan in the future without needing to buy a new router.
Router Location
The location of your router in your home or office can have an impact on the internet speed your devices get.
WiFi Coverage Range
In general, the farther away from your router you are the slower your internet connection will be.
A general rule of thumb for distance from the router and internet speed is: when you double the distance between your internet device and your router, your internet speed decreases by one-third.
The longer the distance between your devices and router, the longer the radio waves between the two devices have to travel. This greatly increases the chances of something disrupting the signal. Some examples of things that can block your WiFi signal are:
- Concrete and brick walls
- Thick wooden walls
- Water (e.g. aquariums or water-based heating systems)
- TVs
Because WiFi signals struggle to get through these things, it’s smart to keep your router close to the devices that will be using it.
In situations where your WiFi signals don’t reach to all the areas in your home or office that need an internet connection, you can use a signal repeater or mesh router to increase your WiFi coverage. You can learn more about those devices here.
If most of your internet devices are in the living room, make sure your router is in an open area in your living room. The closer you are to the router when using WiFi, the less chance there is of objects disrupting the signal.
Easy enough right?
Router Placement
The placement of your router is important when it comes to your internet speed.
As previously stated, you need to make sure the signals from your router aren’t blocked by the surrounding environment.
I can’t count the number of times I’ve seen routers behind TVs, in closets with closed doors, or even underneath couches.
Here’s a good example:

The router in the picture above was secured to the wall of a closet.
Please don’t be this person.
The people using the internet in your house will thank you.
I’m sure you can guess by now that you want your router placed in an open area with minimal obstruction. Even better, placing your router on an elevated surface will improve your WiFi signal as well.
WiFi Channel Selection
Most of today’s routers provide WiFi signals on two different frequencies: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Each of these frequencies will show up as their own WiFi network you can connect to.
These two radio frequencies are divided into channels that allow your wireless devices to send and receive data.
The 2.4 GHz band has 11 WiFi channels and the 5 GHz band has 45 channels that can be used.
What does this have to do with the speed of your internet?
Well, if many devices are using the same WiFi channel at once, it will slow your internet down.
Your router typically chooses your WiFi channel automatically when it’s first turned on and set up. While this might be great at the beginning, this channel can become congested as time goes on. For example, you could have new neighbors move in and start using the same WiFi channel on their network.
How Can I Find the Best WiFi Channel?
If your router and other network equipment are suitable for your internet plan but you’re still experiencing slow internet speeds, the wireless channels you’re using might be the culprit.
If this is the case for you, I would recommend downloading an app that can analyze WiFi signals. A free tool that I use is Acrylic Wi-Fi Home.
Acrylic Wi-Fi Home will show you all the wireless networks in your immediate area and the channels they’re using.
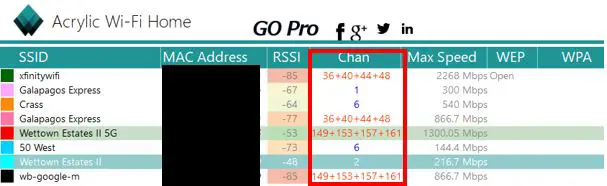
As you can see, it looks like my 5G network (Wettown Estates II 5G) is using the same channels as the nearby “wb-google-m” network. Is this a cause for concern? Only if my internet is experiencing slow speeds.
Let’s dig deeper.
When you click on a network in Acrylic Wi-Fi Home, it’ll show you how it ranks in certain criteria.
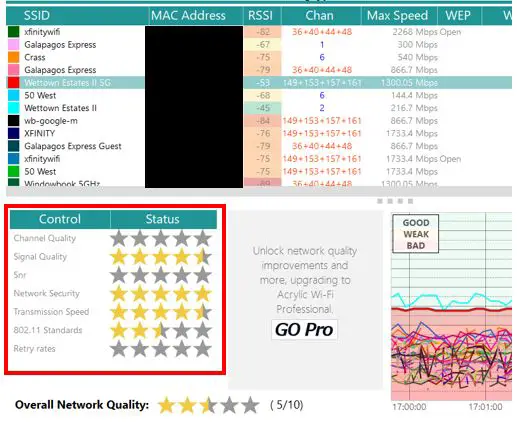
As you can see above, although my 5G network shares the same WiFi signals as another network, the signal quality and transmission speed rank very highly. I don’t need to make any changes to my WiFi channels because I’m not experiencing slow internet speeds.
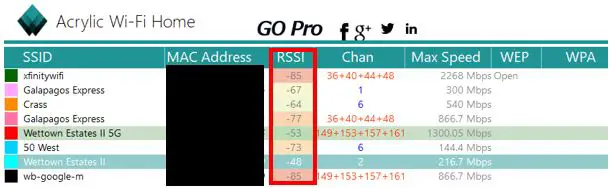
Another key tip about Acrylic Wi-Fi Home is that the RSSI column shows you the strength of your wireless signal in a particular area of your house. The lower the negative number, the stronger the signal is. This will help you determine if there are any areas of your house where you get a weak WiFi signal.
How to Change the Channel on Your Wireless Router
If your investigation reveals that you need to change your WiFi channels (or you want to experiment with them), you can do so by logging in to your router. You can get to your router screen by entering your router’s IP address in the search bar of your internet browser. For me (and many other routers), my router’s IP address is 192.168.0.1.
Also, the sticker on the router itself may indicate how you can log in.

I have a Tp-link router, so I can also log in to my router by typing https://tplinkwifi.net into my browser.
The interface of everyone’s router might be a little different, but the settings should be similar.
Once I log into my router, I can access my WiFi channel settings by navigating to the Advanced Wireless Settings tab.
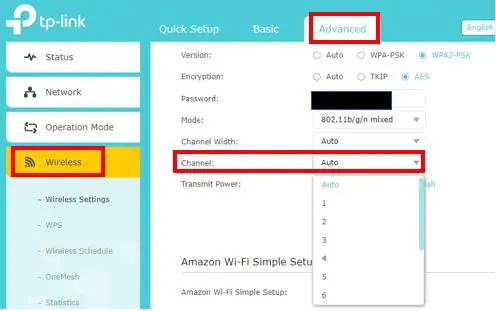
On this page you’re able to manually select the channels that your WiFi network is using. Many routers will be set to auto channel selection by default, but if you’re experiencing a slow internet connection feel free to manually try a few different channels. You can always change them back at a later time so it doesn’t hurt to try a few different channels. For 2.4 GHz networks it’s said that channels 1, 6, and 11 perform the best, so you may want to try those first.
Router Firmware Needs to Be Updated
The last way that your router can affect your internet connection is if it has outdated firmware.
The firmware of your router is the software that’s coded onto it.
As I mentioned earlier in this post, there are advances to wireless technology happening all the time. To prevent you from having to buy a new router every time a small advancement is made, router vendors push out firmware updates for you to install.
If new router upgrades are developed by the vendor and you don’t upgrade your router, your internet performance may suffer. These upgrades may fix bugs or inefficiencies in the way your router operates, so you want to make sure it’s up-to-date.
How to Update Router Firmware
You can check to see if your router has firmware updates available by logging in to your router again.
On my router I navigate to the Firmware Upgrade screen in the System Tools tab.
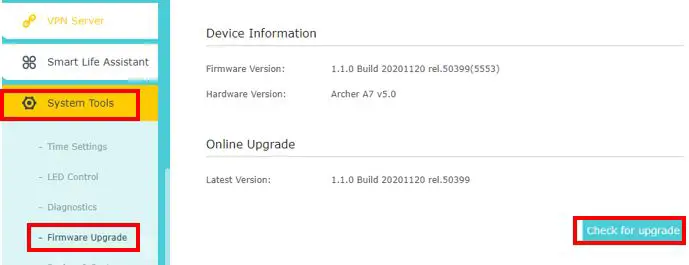
By clicking Check for upgrade, the router will check to see if there are any firmware upgrades available for it. If there are, you’ll be able to download the new firmware and restart your router.
When you’re going to upgrade your router firmware, it’s very important that you connect the internet device you’re using to your router with an ethernet cable. If you lose an internet connection while you’re updating the firmware of your router, your router may no longer work. An ethernet connection will ensure you don’t lose connectivity during the upgrade.
What Router Do I Need?
Now that we’ve discussed how a router can affect your internet speed, let’s make sure you have the right one.
So how do you know if your router fits your needs?
It’s always best to start by identifying the speed of your internet plan. This will help you determine if your router supports the plan you have.
You can find the maximum internet speed of your plan by looking at your most recent bill or by calling your ISP.

As you can see, my internet plan provides a maximum download speed of 600 Mbps.
Once you know the maximum internet speed of your plan, you should look up the specifications of your router. If you’re not sure of your router’s make and model, you can usually find that information on a sticker on the router itself.

I have a Tp-link Archer A7 AC1750 router. With this information, I can go online and search for the specs of this router.
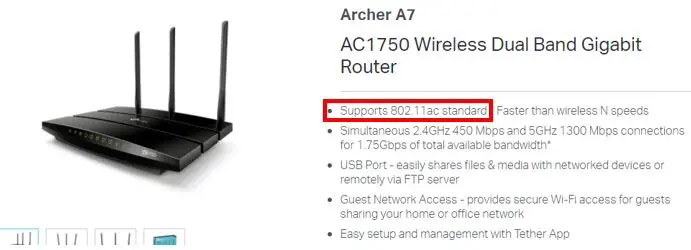
On Tp-Link’s official website it provides the specifications for the Archer A7 router. The Archer A7 router supports the 802.11ac standard for WiFi speeds. In looking back at our WiFi standards diagram, we can see that the 802.11ac standard supports internet speeds up to 1.3 Gbps.
With my router supporting speeds up to 1.3 Gbps and my maximum internet speed being 600 Mbps, I know that my router won’t be slowing down my internet connection. It’s now on me to make sure my router:
- Uses WiFi channels that aren’t congested
- Is located in an open area away from obstructions (e.g. my TV)
- Isn’t far from the devices that will be using the internet most
- Has updated firmware
What if I Have to Get a New Router? What Router Should I Get?
If your current router is slowing down your internet connection, you’ll either have to scale back your internet plan or get a new router.
Assuming you’ll get a new router, it’s important to take into consideration everything that was discussed in this post.
Some of the questions you’ll want to ask yourself are:
- What internet speed does my router need to support?
- Are my internet needs going to change in the near future?
- Do I want to future proof my router so I don’t need to buy a new one if I upgrade my internet plan?
- How large of a living area do I need to provide internet access to? How many floors is it?
- If I have a large area or multiple floors, do I need a WiFi range extender or should I get a mesh router network?
- What’s my budget for a new router?
- Do I want a standalone modem and router or a modem/router combination?
Answering these questions will help you decide what kind of router you need.
If you haven’t guessed, I personally love my TP-Link Archer A7 router. It’s very inexpensive, and I know it has me covered in the future if I want to upgrade my internet plan.
If you’re willing to spend a little more money on your router, the Linksys EA6350 router is another popular choice.
If you do your homework and make sure your router meets all the needs of your unique situation, there’s a high probability that you’ll love your home internet experience.
Wrap Up
Has anyone had any problems with their router slowing down their internet connection? I’d love to hear your stories. Feel free to post your experiences in the comment section below, or send me an email via the Contact Me page.
If you’d like to read more about similar topics, check out the following articles that I’ve previously published:
Can an Ethernet Cable Slow Your Internet Speed?
Does Your Modem Affect Your Internet Speed?
Does an Old Computer Affect Your Internet Speed?

Leave a Reply