This post contains affiliate links.

If you’ve spent time configuring your home network, you’ve probably seen the term MAC address when referring to your devices.
MAC stands for Media Access Control, and a MAC address is used to help identify the devices on your network.
What can be harder to understand is which of your devices have MAC addresses, and which ones don’t.
This question is frequently asked about routers. Unfortunately, the answer may be a little more complicated than you would expect.
All routers have MAC addresses associated with them. In fact, routers will have a MAC address for each of their network interfaces. As a result, most routers have three MAC addresses: one each for their internet, wired local network, and wireless local network interfaces.
In this post, I’ll break down the three common MAC addresses associated with routers. I’ll also detail how to go about finding what your router’s MAC addresses are.
Let’s dive in.
Why Does a Router Have Three MAC Addresses?
You might be surprised to find out that most routers have three MAC addresses. Why can’t one address be used for your device?
The main reason for this is that each of the network interfaces on your router is identified individually. The three network interfaces on your router are its:
- Internet (public) interface
- Local wireless (WiFi) interface
- Local wired (ethernet) interface
The internet interface on your router is used to allow your devices to communicate with the rest of the internet. In this sense, it’s the only interface on your router that’s accessible by the rest of the internet.
This is also known as your router’s WAN port. It’s usually found on the back of your router.

The local wireless (WiFi) interface on your router is what your router uses to broadcast a WiFi network signal to your devices. Your devices use this network interface to get wireless internet connections from your router.
This interface is connected to the antennas on your router.

The local wired (ethernet) interface on your router is for the ethernet ports on your router. These ethernet ports allow you to connect your devices to your router with an ethernet cable.
You’ll usually see at least four of these ethernet ports on the back of your router.
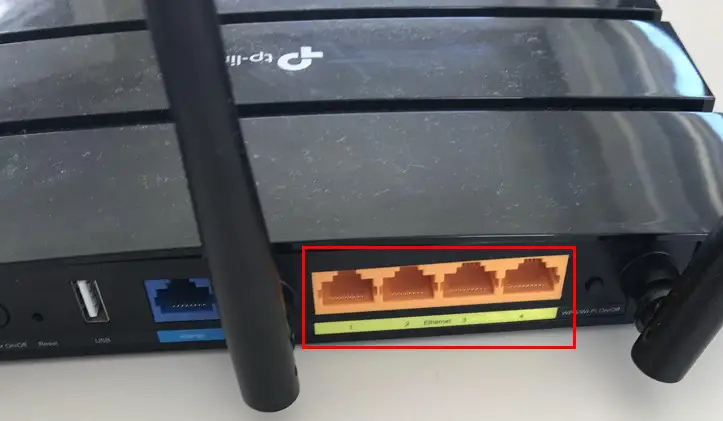

What’s important to realize is that these interfaces are actually all separate devices within your router. That’s part of the reason why they’re identified individually with separate MAC addresses.
The other part of the equation is that by having separate MAC addresses, it helps ensure that the traffic on your network is sent to the right place. We’ll discuss this more in depth later on.
How to Find a Router’s MAC Addresses
When it comes to determining what your router’s MAC addresses are, you have a few options.
You’ll be able to figure out one of your router’s MAC addresses by looking at the sticker on the device. You’ll have to find out the other two addresses by accessing your router’s settings.
I’ll explain both of these methods for determining what the MAC addresses of your router’s interfaces are.
How to Find One of Your Router’s MAC Addresses by Looking at Its Sticker
Ok, the first way to find out one of your router’s MAC addresses is by looking actually looking at your router.
Somewhere on your router, there should be a sticker providing some basic information about the device. You’ll most likely find the sticker on the bottom of your device. Here’s the sticker on my router.

The sticker usually includes information like the default IP address, default wireless network names and passwords, and the make and model of your router.
If we take a closer look at the sticker, we’ll see that there’s a MAC address listed as well.

It’s important to note that this MAC address pertains to the local wired interface on the router. In other words, it’s the MAC address for the interface connected to the router’s ethernet ports.
To find out the other two MAC addresses of your router, you’ll have to go into your router’s settings.
How to Access Your Router’s Settings to Find Out Its MAC Addresses
In order to find out your router’s other two MAC addresses (or see all three at once), you need to log in to your router.
To do this, use an internet browser to access the settings login page for your router. If you’re unsure of this location, this is sometimes listed on the sticker on the device as well.
Here’s where this location is listed on my router’s sticker.

In entering this location into a browser, you’ll be able to log in to your router’s settings with the username and password you’ve set up for your device.
If you’ve never changed the username and password for your router, you can find the default settings in your router’s user manual, or by searching online.
As a side note, if this is the case for you, make sure you change your router’s login password to something only you know. It’s extremely insecure to use the default password for your router’s settings.
Ok, so you’ve logged in to your router’s settings. This’ll probably take you to your router’s main settings page.
From here, I had to go to the advanced settings tab to see the MAC addresses for my router.
In the Advanced Settings tab, I’m able to see all three MAC addresses for my router’s interfaces.
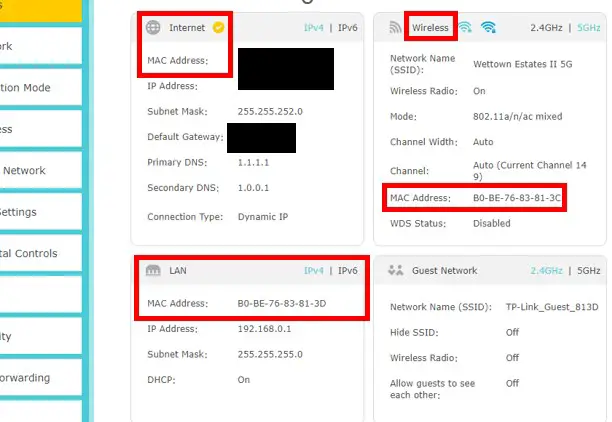
As a note, I have hidden the MAC address and IP address of my router’s public interface for security reasons.
If you’re interested in all of your router’s MAC addresses, it’s easiest to log in to your router’s settings. It serves as a one-stop shop for everything you need without having to get out of your chair.
What Are Router MAC Addresses Used For?
As I mentioned earlier, a router’s MAC addresses are important because they make it easier to find out where traffic in your network is supposed to go.
How exactly do they do this?
This has to do with their relation to how IP addresses are assigned.
In order for an IP address to be assigned, it needs to be associated with a MAC address.
Without getting too technical here, this is because the MAC address of an interface is used by local devices that are physically connected to it, while an IP address is used by devices that aren’t physically connected to the interface.
MAC Addresses Are Used for Local Communication
Think of a MAC address like a local mailing address, while an IP address is the full mailing address for a house.
If your neighbor down the street asks you where you live, you can just tell them the name of your street and your house number. With that information, your neighbor will be able to send you a letter because they’re familiar with the local area.
In this example, the local address of your home would be the MAC address of an interface.
On the other hand, in order to tell your friend who lives in another country where you live, you need to provide more information. In this case, you’d have to send them your full mailing address (including a zip code and state) in order for them to send something to you.
In this case, your full mailing address is equivalent to the IP address of an interface.
What’s important here is that you can’t provide the full mailing address of a house (e.g. zip code and country) without knowing the local components of it (e.g. street name and house number). This is why MAC addresses are such an important component of your router’s interfaces. An interface must have a MAC address in order for it to be assigned an IP address.
With this information in mind, it’s easy to see how router MAC addresses are used. They’re used as mailing addresses by the devices on your local network that’re physically connected to your router. This enables these devices to send their network traffic to the right location.
Without MAC addresses assigned to each interface, it would be impossible for your local devices to know which interface to send network traffic to. The same goes for devices that aren’t physically connected to your router. If a given interface didn’t have a MAC address, it wouldn’t have an IP address to send information to.
If a device didn’t know the right local location to send its traffic to, it would greatly slow down the communication between devices internal and external to your network, if not halt it entirely.
Wrap Up
Congratulations, you now know everything there is to know about your router’s MAC addresses. If you have any questions about this information, please drop a comment below.
If you’re interested in learning more about similar topics, check out some other relevant posts I’ve written:
What Router Do I Have? How to Find Out
How Many IP Addresses Should a Router Have?
Why Do Routers Have Multiple Antennas?
